Rugby - Rugby history
Rugby- Olympic Sports
![]()
History
"Rugby is a small town 300 miles from London.
In 1823, the Rugby School was one of those Public Schools, very well attended, although not the prestige of Eton or Harrow. It took the arrival in Rugby, some twenty years later, the famous educator Thomas Arnold, for sport, and football-rugby in particular, become part of the education of students. On the grounds of Rugby School around 1600 m2, the famous 'Bigside', students played according to certain conventions transmitted by oral tradition with a ball more or less round, due to the shape of the domestic pig bladder . They could receive the ball in his hands if he came directly from a kick (Case fly today) or if the pick was completely motionless on the ground, but the kick immediately because he was banned from running in the relating to the opposing goal. This would have made William Webb Ellis in 1823, a true pioneer of this game! The trophy of the World Cup bears his name.
This game a few years will spread not only throughout England, but even in Scotland, Ireland and win in Wales. And not staying schoolboy's amusement, but becoming in the fullness of the word sport being honored and practiced by men of "society".
The International Rugby Football Board was founded in 1886 by Scotland, Ireland and Wales (91 affiliated countries).
The International Rugby Board (IRB) "IRB" for a particular purpose, promotion, promotion, development, expansion and management of the rugby game. He is responsible for drafting and interpreting statutes, regulations and rules of the game
Federations founding of the IRB Rugby Football Union (England), Scottish Rugby Union (Scotland) Irish Rugby Football Union (Ireland), Welsh Rugby Union (Wales), Australian Rugby Football Union (Australia), New Zealand Rugby Football Union (New Zealand), South African Rugby Football Union (South Africa), French Rugby Federation (FFR).
The Council Board is composed of 26 persons (two representatives from each federation + parent representative federations: Argentina, Canada, Italy, Japan, +1 representing each regional association: Africa (CAR), North America (NAWIRA ), South America (CONSUR), Asia (ARFU), Europe (FIRA) and Oceania (FORU).
Rugby World Cup Limited (RWC Ld) is led by 5 directors elected by the Council of the IRB. She oversees all global competitions(World Cup, FIFA modne Women World Cup Rugby 7's World Championship under 21, World Championship under 19 years, Circuit World Rugby 7) in all areas: sports, regulatory, commercial and financial.

Some dates
- 1823-1860: early and expansion of the game (in 1843 founded the first club in Britain "Guy's Hospital in London).
- 1830-1840: the first rules of this race ball in hand is edited by Thomas Hughes.
- 1851: to facilitate its seizure, the bullet becomes oval.
- 1860-1871: founding clubs and the Rugby Football Union. In 1871 the first official match between England and Scotland in Edinburgh (score 0-1).
- 1871-1877: The game goes to 20. The rules were codified in 1871.
- 1877-1893: the game from 20 to 15 players. Foundation 3 other RFU and the International Board. Division of the North and created the Northern Rugby Union later became.
- 1893-1914: modern game, Dominions intervention. Emergence of French game. In 1900, rugby is entered in the Olympics program in Paris. It will remain an Olympic sport until 1924.
- 1918-1939: new ideas and tactics for world rugby.
- 1924: France meets the United States in Olympic final. Following the match very violent on the field and off, rugby is no longer an Olympic sport.
- 1934: the Federation Internationale de Rugby Amateur was created.
- 1978: France joined the International Board.
- 1991: the first World Cup of Women.
- 1995: start of the open era, rugby is no longer an amateur.
- 1999: First Tournament of the Five Nations Women
- 2000: Italy joined the Five Nations Tour, which now bears the name: RBS Six Nations
- 2009: Rugby sevens became an Olympic sport again. Rugby has been an Olympic sport in 1900, 1908, 1920 and 1924, the rugby sevens will be the 2016 Olympic Games in Rio de Janeiro. Twenty-four teams, half women (288 athletes in total) will participate in the tournament on two or three days. The teams will
ized into two groups of six. The top two teams from each group advance to the semi-finals. Each match will involve two phases of seven minutes.
The first French club was Le Havre Athletic Club, founded in 1872, then came the Racing Club de France in 1882 and the French stage in 1883. The real and sole founder of the sport in France was Georges St. Clair, educated in England, who transformed a group of "schoolboy" anxious only to imitate the horse races, including stables and paris in a sports club athletic. In 1883, on the first game between the only two French teams existing at the time: Racing Club de France and Stade French. Then creates January 31, 1889 the Union of French Societies of Athletic Sports (USFSA) to govern the whole of French sport. The first official game of Team France took place in January 1906 against New Zealand.
The French Rugby Federation was created in 1919 following the breakup of the USFSA (248 072 graduates in 2006).

Rugby in France Is:
- 222 600 members with 4 167 women - 1 715 clubs
- 3 972 referees
- 123 technical staff
- 2756 Coaches
- 16 514 officers club rugby
- 13 772 educators
- 10 teams from France
- 38 levels of competition
- 26 regional committees and 7 boards in the DOM-TOM
- 102 departmental committees
- A National Rugby League was responsible for organizing, managing and regulating the professional sector.
Past Team France
- Olympic Champion in 1900
- Vice Olympic Champion in 1920 and 1924
- 2nd in the World Cup in 1987 (finalist against New Zealand) and 1999 (finalist against Australia)
- 3rd in the World Cup in 1995 (won against England)
- 4th in the World Cup in 2003 (losing to New Zealand) and 2007 (defeat against England)
- 6 Grand Slams in the 5 Nations Tournament (1968, 1977, 1981, 1987, 1997 and 1998)
- 2 Grand Slams in the RBS 6 Nations (2002 and 2004)
- World Junior Champion in 1995 and 2000
- European Junior Champion in 1972
- World Champion University in 1992 and 1996
- World Junior Champion in 1996
- European Champion Women in 1996, 1999 and 2000
- Grand Slam in the RBS Women's 6 Nations 2002.

The France won the first time the 5 Nations Tournament in 1954 tied with Wales and England and for the first time only in 1959. The first Grand Slam French took place in 1968.
All about the Rugby World
There are currently about 1.9 million practitioners worldwide in approximately 80 countries.
South Africa, 361 000, 1 116 clubs - England, 634 000 licensed, 1800 clubs - Argentina, 21 000 licensees, 198 clubs - Australia, 140 000 dismissed, 456 Club - Canada, 47 000 licensees, 175 clubs - Scotland, 13 800 licensees, 275 club - France, 222 000 licensed, 1710 Club - Fiji Islands, 35 000 licensees, 200 clubs - Tonga Islands, 23 000 redundant, 70 clubs - Ireland, 53 000 licensees, 226 clubs - Italy, 36 000 redundant 505 Club - New Zealand, 150 000 dismissed, 550 clubs - Wales, 17 500 players, 212 clubs - Romania, 4 500 licensees, 60 clubs - Zimbabwe 1 000 licensees, 30 clubs
Competition
Two teams of fifteen players each try to score as many points as possible by carrying, passing or kicking the ball. The one who scores the most points is declared the winner.
79 403. ... Record of spectators at the Stade France directed by the match between France and England ... 2002 ... better than the final of the FIFA World Cup between France and Brazil in 1998!
Field
It is a rectangle with a width of 70 m and a maximum of 66 m and a minimum length of 100 m and 95 m more or less.
A record! The aim of the longest history is 91 meters (100 yards), managed by South African Morkel Douglas in 1906 during a match against Middlesex at Richmond, near London.
The balloon
The balloon is shaped oval, not as is commonly believed that because this form is better suited to handle by hand (there was no pass) but simply because the bladder was inside a pig's bladder which had naturally this more or less ovoid. Initially, there was a house capable of producing, the firm W. Gilbert Rugby.
![]()
The ball, when new, should be oval in shape (since 1851), and comprise four panels have the following dimensions:
- Length of major axis: 28 to 30 cm
- Large area: 76 to 79 cm
- Small area: 58 to 62 cm
- Weight: 400 to 440 g
- Pressure: between 0.67 and 0.70 kg per cm.
Since 1995, we can kick the ball from a tee placed 3 inches above the ground.
Equipment Players
The spikes of the shoes of players must be leather, rubber, aluminum or plastic. They must be circular, firmly attached to shoes and meet the following dimensions:
- Maximum length measured from the flange: 18 mm
- Minimum diameter at the base: 13 mm;
- Minimum diameter at the top: 10 mm;
- Minimum diameter of the washer (if it is independent of spike): 20 mm.

Players must wear a clearly visible number on their jersey.
The numbering of jerseys should be the following:
- Rear: 15
- Three-quarters (from left to right): 11, 12, 13 and 14
- Half of Operation: 10
- Scrum Half: 9
- Forwards (three courses, two, three):
Third row (lr): 6, 8 and 7
Second line: 4 and 5
First line: 1, 2 and 3
or
- Forwards (training three four, one):
Third line: 8
Second row (lr): 6, 4, 5 and 7
First line: 1, 2 and 3.
The number of players
A match is played with fifteen players per team maximum. Seven replacements are allowed.
Replacing an injured player on bleeding may be temporary but if it can not resume the match within fifteen minutes, his replacement becomes permanent.
The duration
The duration of the game is 80 minutes. The game is divided into two stages.
At halftime, the teams change ends and a break up to ten minutes in France, in elite 1 and 2 and in international matches, and five minutes for the other
ISIONS.
The main rules
New Rules
The IRB has established new rules for a test period of 12 months. Thirteen of the twenty-six new rules came into force on 1 August 2008, including the Top 14. One concerns the match officials, both the maul, seven key and alignment, both the scrum and the corner posts.

They are:
Rule 6 - Match Officials
1. The assistant referees can now help the referee by any means agreed with it.
Rule 17 - Maul
2. The rule requiring the maintenance of the head and shoulders above the hips is removed.
3. The players are allowed to defend at a maul by putting it down.
Rule 19 - Key and alignment
4. If a team sends the ball into his 22 yards and the ball is then kicked directly into touch, there is no gain of ground. A key is given to the opponent at the spot where the kick was booted.
5. At a quick throw-in, the player taking the throw-in can throw the ball is perpendicular to the sideline or back towards his own goal line.
6. There is no limit to the number of players each team can participate in alignment. Each team will be freedom of choice concerning the number of players to be in alignment.
7. The receiver must stand two meters from the alignment.
8. The player opposite the thrower must stand in the area between the 5 meter line and touch line but must also be held at two meters of alignment.
9. Players alignment can perform an action pre-gripping on a jumper before throwing the ball.
10. It is authorized to raise a player in the lineup.
Rule 20 - scrum
11. Establishment of an offside line located 5 m behind the partner's feet farther back from the fray.
12. Identification of lines out of the game for scrum-half. It is the only player the power to advance the progress of the ball.
Rule 22 - Corner Posts
13. The corner posts are no longer considered part of the key purpose, unless the touch down is made against the post.
How to play and kick
1. Part begins with a kickoff after which any player involved may at any time, provided he does so under the rules:
- To catch or pick up the ball and run into the bearing;
- Pass the ball to another player behind him;
- Slapping the ball;
- Tackle an opponent carrying the ball;
- Push a partner or support the ball carrier;
- Falling on the ball;
- Take part in a ruck or a "maul".

2. Kickoff is set up:
by a drop kick gave the middle line of 50 meters, or behind that point, the team who must start the game or the opposing team to play resumed after the mid - time or by the defending team after she cashed points.
3. The ball must be kicked to the right place if he is not so, the kick is retaken.
4. The ball must reach the line of 10 meters opponent, unless it is previously played by an opponent if he is not so, or the kick is retaken, or a scrum is ordered, the center of the field chosen by the adversary. If the ball reaches the line of 10 meters and then the wind pushes the game continue.
5. If the ball falls directly into touch, touch in goal, on or beyond the dead ball line, the opposing team can accept the kick start to kick or receive a free ordered to center field.
6. The kicker's team must stand behind the ball at kickoff. If it is not, a scrum is ordered at midfield.
7. The opposing team must stand on or behind the line of 10 meters. If a player is in front of the line or load before the ball has been kicked, the kick is retaken.
.jpeg)
Hall Of Fame
Fifty legends of world rugby have been admitted to a very select Hall of Fame in London. Among them are six French rugby: Jean Prat , Jo Maso , Jean-Pierre Rives , Serge Blanco , Philippe Sella and last admitted in 2006, André Boniface
Coaches XV de France
1963-1967: Jean Prat
1968-1972: Fernand Cazenave
1973-1980: Jean Desclaux
1981-1990: Jacques Fouroux
1990-1991: Daniel Dubroca
1991-1995: Pierre Berbizier
1995-1999: Jean-Claude Skrela
1999 - 2007: Bernard Laporte
Since November 2007: Marc Lievremont
The points earned
1. Trial
A test is marked first by making a touchdown on the ground in the opposing goal.
A trial may be granted if the referee believes it was probably marked antijeu without the opposing team.
One test is worth one point in 1871, 3 pts in 1894, 4 points in 1971 to 5 pts in 1992.

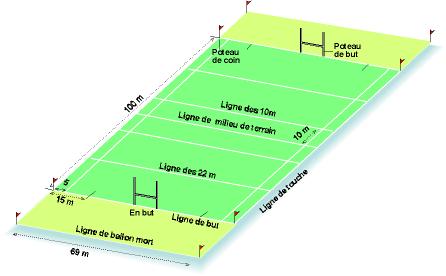
2. Purpose
A goal is scored by sending the ball to any point in the field of play, over and above the crossbar and between the goalposts opponent, using a kick placed or dropped - except kickoff, the stroke reference or free kick - and without the ball touching the floor or a partner kicker.
3. The score
It is evaluated as follows:
- Test: 5 points
- But after test (conversions): 2 points
- Goal kick Penalty: 3 points
- But on drop kick (drop-goal): 3 points
With a goal post.
Penalty try
A penalty try will be awarded in the middle of the goal posts when antijeu without the defending team:
- A trial would probably have been scored,
- Or it would have been scored in a better position than where it was scored.
Touched to the purpose
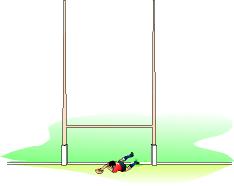
1. He is "touched in order" when a player makes the first one hit the ground in his own goal.
2. After a touchdown in goal, play shall be resumed by a stroke of reference, a 5-meter scrum.
New rules from 1 January 2007
To minimize injury to mixed: the term "Crouch, hold, engage" (lean, hold you, hire you) is no longer valid since 1 January 2007. Henceforth, it will be "Crouch, touch, pause, engage" (lean, touch you, wait, commit). Now, the pillars affect the arms of their opponents with the aim of reducing the distance between the two packs and the intensity of their entry.
Melee after flattened in the in-goal
When there is doubt in the determination of the team that was, first, a touchdown on the ground in the in-goal, a scrum is ordered at 5 meters from the goal line, opposite where the affected land has occurred. The attacking team will benefit from the introduction.

1. After testing, the team who scored a try in the right order, either by a kick placed either by a drop kick, from a line passing through the point where the test was scored.
If the team who scored the test does not attempt the goal, the game will be resumed by a drop kick at the center of the field, unless the play time is over.
2. If the goal is attempted:
- The kick should be given without delay,
- Any player - including kicker himself - can place the ball
- The team's kicker (with the exception of "underwriter" if any) must be behind the ball when it is booted,
- If the ball is kicked in the hands of the distributor without the ball is in contact with the ground, the kick is zero,
- The opposing team must be behind the goal line until the kicker begins his run and begins its kick. From that moment, the opposing team may charge or jump to try to prevent the goal.
In-goal
The in-goal is the area of land bounded by a goal line, the sidelines of the goal and dead ball line.
The goal line and goal posts are part of the in-goal, but the sidelines of the goal and dead ball line are not included.
1. Key Goal
There are key goal when the ball or the player wearing it, touches a corner post or a touchline goal, or soil, a person or object, beyond this line. The flag is not part of the corner post.
2. Scrum five meters
- If a player carrying the ball in the in-goal is given so that it is impossible to make a touchdown on the ground, a scrum is formed 5 m from the goal line, and opposite the where the player was held. The attacking team will benefit from the introduction. The same applies to the following cases:
- If a player of the defending team heels, boot, gate, or pass the ball in planning its own in-goal and the ball is considered dead, unless a test is scored or a player plans, or spear, voluntarily ball in hand from the playground, in key purpose or beyond the dead ball line.
- If the kick of a defending player, being in his in-goal is "blocked" as:
- The player himself has carried the ball from the playing field in the in-goal,
- A defending player is to penetrate, and the ball is then subjected to a touchdown in purpose or will in key purpose or dead ball.
- If a defending player, carrying the ball into the playing field, is driven into his in-goal and there is a touchdown in goal.
.jpeg)
- If, in ruck or scrum, a team defending with the ball is pushed in his in-goal and that, before the ball emerges, a defending player is the first one hit the ground in the in-goal .
Apart from cases where a test or a goal is scored, if an attacking player boot, gate, or pass the ball well in penetrating the in-goal opponent (either directly or after touching a defender who does not try voluntarily stop, to catch or kick it) and that is:
- It hit the ground by a player of one or the other team, or
- He goes into key goal or goes beyond the dead ball line,
A kick return will be granted. It can promote quick references. This reference is possible without all the players the team is seen behind the line of 22 meters.
Now when a ball is kicked into the in-goal or dead ball after the referee deemed it if the kick was intentional, the opposing team can choose between a reference to the 22 meters and a scrum developed Departure of kick, with an introduction to it.
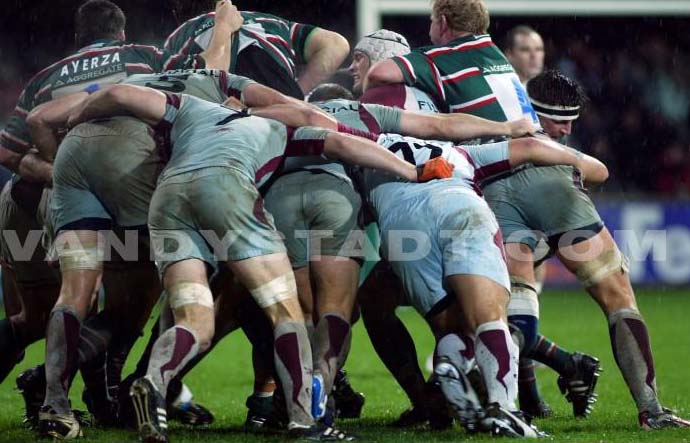
Scrum
A scrum - which can take place in the field of play - is comprised of players from both teams linked to allow the balloon to be launched on the ground between them.
The first line must bind to their rivals
To avoid crumbling shoulders must be kept above the basin
The collective thrust must be axial
Now the battle must be formed by eight players. These players will not have the right to detach before the release of ball. This rule gives more scope for three quarters and also fix the third line.
Ruck and maul
1. Ruck
A ruck, which can take place in the field of play, occurs when the ball is on the ground and one or more players from each team are in contact, standing on their feet, surrounding the balloon is among them.
Any player joining a ruck must bind with at least one arm, passed around the body of one of its partners ruck.

Maul
A maul, which can take place in the field of play, is formed by one or more players from each team standing on their feet in contact, surrounding a player carrying the ball.
A maul ends when the ball is down or the ball - or the player who wears it - has emerged from the maul, or when a scrum was ordered.
The light
1. There are "held" when a player carrying the ball in the field of play, is seized by one or more opponents and, while it is so light, it is put to the ground or the ball touches the ground.
2. A player "light" and tackle, whether on land, must release the ball immediately, without playing any other way whatsoever, and get up or move away. He must play the ball or hold it in any manner whatsoever until it is back on its feet.
The key
1. Release button
There are key when:
Not being worn by a player, the ball touches the touchline or the ground or a person or object on or beyond this line, or when being carried by a player, ball, or the player who wears it, touches the touchline or the ground beyond.
If the ball is out of touch, a player finding himself in touch may kick the ball or propel with his hand, but the take over.
2. Play button
The line throw-in is an imaginary line in the field of play, forming a right angle to the sideline and passing through the point where the ball must be handed in.
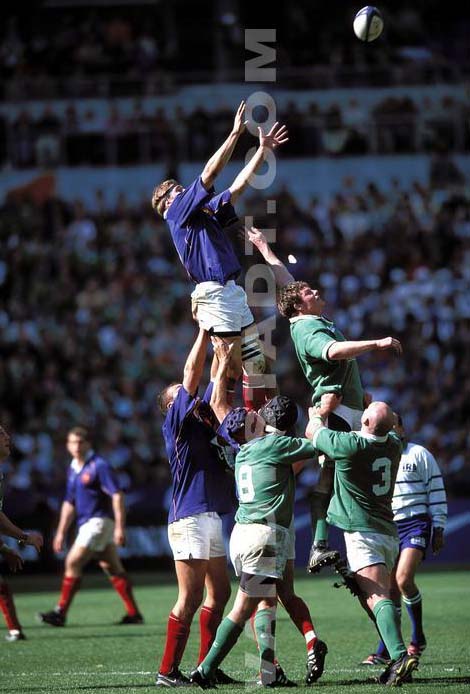

3. Training of key
The key is constituted by at least two players from each team standing in two simple lines parallel to the line of throw-in, ready for what the ball is thrown between them. The players are well prepared so-called "alignment".
The key support is possible but only when the ball was put back into play and the player has started his jump. The elevator key is no longer sanctioned. The player may catch or deflect the ball with the inside arm. Only two hands must be above the head. In short: protection and support of the player who jumps are allowed.
Stop volley (brand)
Stopping air broadcast may be made without a foot on the ground. The defender can then jump to catch the ball as the striker made.
1. A player makes a stop volley when - being on the side of his in-goal from the line of 22 feet - he catches the ball well from a direct kick from an opponent, and at the same when he shouts: "Brand!"
A stop volley may be obtained even if the ball into his path, hit a goal post or bar
crossbar. It can be done in the in-goal.
2. A free kick will be awarded on a stop volley.
The free kick is kicked by the player who made the decision to fly, unless he was injured on this occasion. If he is unable to give this kick in the minute following a scrum is formed at the point mark and his team will benefit from the introduction.
If the stop flight takes place in the in-goal, any melee that can possibly result will be ordered to five meters from the goal line on a line passing through point mark.

A figure
72: the weight difference in kilograms between the Springboks pack (total: 906 kg, average 113 kg) and that of French (total 834 kg, average of 104 kg).
The main faults and penalties
Offsides
There are offside if:
- A player is in front of his teammates in possession or to a teammate who comes to play.
- During a ruck or closed, or if there is lead in front of the line offside. Only the No. 8 player is allowed to detach and pick the ball free.
- A player not involved in the key is offside if, before the key has expired, it remains ahead or in front of the line offside.
Exceptions:
- When an offside player can not avoid being hit by the ball or the player who wears it, he "accidentally offside". The game will continue unless the team derives an advantage, in which case a scrum is formed at this location.
- A player who receives a forward pass is not accidental offside.
- If, because of the speed of the game, an offside player can not avoid being within 10 m from opponent waiting to play the ball, it will not be penalized provided he withdraws immediately and without intervening on the opponent.

Forward and forward pass
There are before-when the ball goes to the dead ball line after the opponent, a player has lost possession, or that the player has pushed or hit him with his arm or hand, or has hit the arm or hand of a player and it touches the ground or another player before being rechecked by the first player.
There goes-forward when a player carrying the ball, throws or passes towards the dead ball line opponent. A throw-in to the key is not a forward pass. If the ball is not thrown or passed forward but bounces forward after hitting a player or the ground, not a forward pass.
A pass, projection or drop ball will be pre-judged that it is clearly the case under the rule. If there is any doubt, the game will continue.
The in-front, or forward pass, should not be intentional. In any case, the penalty will be: kick a penalty at the place of fault minimum 15m from the touchline.
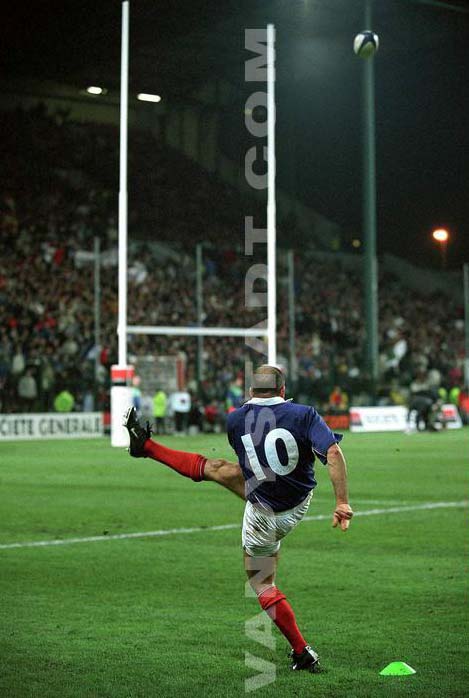
Kick penalty
A kick is a penalty kick awarded to the non-offending team when certain rules were violated by the other team.
It can be given by a player of any team not at fault, as he wishes (kick placed, dropped or stolen), provided that the kicker:
- He has the ball in hand, in the plans before kicking
- If the ball is on the ground to propel the foot, a distance of no discernible mark. In the case of a kick set, he can leave his hand on the ball while the boot.
The non-offending team may choose a scrum developed brand, instead of kicking, it will benefit from the introduction.
Players who are not quick to ten meters on a penalty played, can now be called into play only after having made the effort to fall back on that distance.
To kick a penalty, the striker will have more than one minute to attempt a conversion or penalty from the time he expressed to the arbiter his intention to kick.
Free kick
A free kick is a kick awarded to stop stolen or given to non-offending team after violation of certain rules from the other team.
On a free kick, the kicker can not himself attempting a goal before the ball has been played by another player.
Where it is awarded following an infringement, it can be kicked by any player.
It can be booted in any form (kick placed, dropped or stolen), provided that the kicker:
- He has the ball in hand in the plans before kick:
- If the ball is on the ground, propels the foot with a distance of no discernible mark.
In the case of a kick set, he can leave his hand on the ball while the boot.

Penalty
- The yellow card: the player is ejected for 10 minutes. Two yellow cards equal a red card. The player will be excluded for the duration of a match.
-If a player first line is temporarily excluded, any player on the team can leave the land to make way for a replacement duly trained and experienced to play the front line.
- Red card: A permanent expulsion.
Rugby 7
Rugby 7 is as a variant of the XV. A game faster, more fun, more passionate, which requires different qualities.
He was born in 1880 in southern Scotland in the small town of Melrose. Ned Haig, the village grocer, practiced rugby within the club premises "the Melrose football club." In order to return the money in the coffers of the club, he planned to organize a tournament involving many clubs around. To minimize the costs of hosting and organizing, he decided to reduce the number of teams and length of matches and the Rugby 7 has emerged. The first tournament took place in April 1883. The tournament in Melrose still exists under the name of "Melrose Seven".
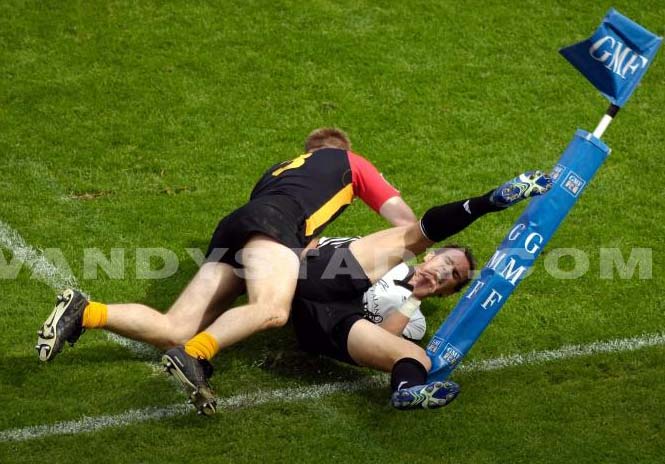

The rugby 7s is now widespread throughout the world and will return to the Olympic Games for Rio de Janeiro in 2016. . The new world circuit comprises eleven tournaments. The world champions are in under Fiji.
The basic rules are the same as the union, including the size of the field, apart from 5 specific rules:
- The duration of a match is 14 minutes, except for the final (20 minutes). They must be
ized into two half-time of 7 minutes. Teams must switch sides at halftime which should not last more than a minute (two for the final).
- In case of a tie, two extensions 5 minutes départagent two formations on the principle of sudden death, which marks the won and the meeting is over.
- The team with the transformation should try the test foot this attempt should be made by a drop kick located on a line parallel to the sidelines through the place has been marked the trial.
- The battle must be made of three players from each team forming a first line. They must remain bound until the end of the melee. In a melee, the head of a player should not be side by side with that of a player of that team.
- A team consists of 7 players: 3 front, 3 three-quarter and one half.
Three replacements or substitutions are allowed!
The allocation of points:
- Between 1883 and 1890, only penalties and tests count for score. The teams consist of a rear, 4 front and 2 three quarters.
- After 1890, the team consists of 3 forwards, 3 three-quarters, 3 three-quarter and one half.
Allocation of points: 2 for testing, 3 for processing, 4 for a drop goal.
The events in the rugby 7 are:
Dubai Open (December) - Tournament of Stellenbosch (December) - Tournament of Mar del Plata (January) - Tournament of Punta del Este (January) - Wellington Classic (February) - Tournament in Australia (February) - Tournament of Suva ( February) - Tournament of Hong Kong (March) Tournament in Japan (April)
Since the 98/99 season, these big tournaments and other less important part of the same global competition, the World Series of Sevens.
The World Cup is held every four years since 1993.
The winners:
1993 (Scotland): England - 1997 (Hong Kong): Fiji - 2001 (Argentina): New Zealand - 2005 (Hong Kong): Fiji - 2009: (in Dubai) Wales
Rugby Women
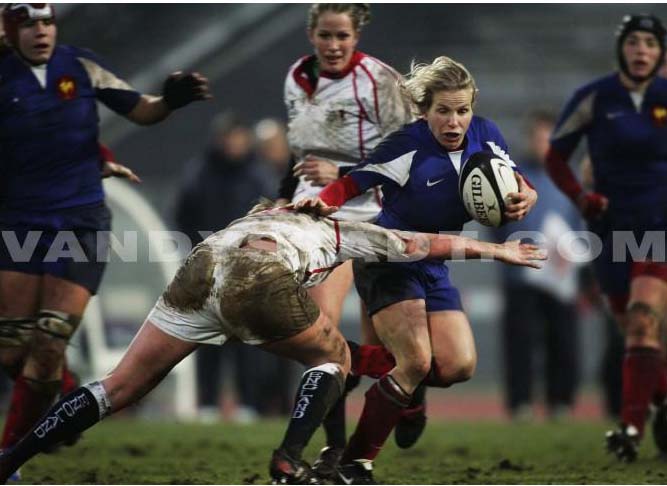

Important dates:
- 1908: First meeting of women's rugby in France
- 1917: Alice Milliat founded the Federation of Women Sport
- 1919: Athlete Elaine Burton caused a scandal in official athletics championships in England, by daring to compete in 'shorts'.
- 1921: Foundation of the International Women's Sports Federation. Alice Milliat is president. Women still do not participate in the Olympics.
- 1928: first participation of women in the Amsterdam Olympics despite opposition from Pierre de Coubertin.
- 1965: first female rugby teams based in France, exit the "bar".
- 1970: Founding of the French Rugby Association (ARF) female.
- 1972: creation of the first championship of France Women's Rugby.
- 1983: AFR receives approval from the Ministry of Sports.
- 1984: AFR becomes the French Federation of Women's Rugby.
- 1988: first European Cup of Nations women's rugby between France, Italy, Holland and British selection. The French prevail, beating three other teams.
- 1989: Women's Rugby integrates the FFR.
- 1991: first World Cup women's rugby won by the United States ..
The women's rugby is structured in three
ISIONS comprising some 80 clubs. He practiced with the same rules as rugby men. The first official edition of the World Cup was held in 1998. The European Championship is held every year except the years of WorldCup. The Five Nations tournament has existed since 1999 and VI Nations since 2000. The team of France in 2002 has achieved his first Grand Slam followed by a second in 2004!
Copyright Sportquick/Promedi






















