| Happy Birthday : |

Weightlifting - Olympic Sports
![]()

We find in games of ancient Greece, the events of "halteria" athletes were raised in each arm of the masses of lead. Since then, men have continued to measure that raises the most burdensome.
Triat Hippolyte (1812-1881) is the true pioneer of weightlifting. Born in the south of France, orphaned at 4 years old, abducted by gypsies to 6 years, it is first tightrope walker, and then at the age of 13 years and presents, in a Spanish company and its two son, a number of plastic poses and lifting weights. Accident at the age of 16, he entered the Jesuit College of Burgos for a period of six years he enriched his knowledge that hitherto were mainly practical, he then resumed his work as an artist and business activity ' athlete, he was a big success in Spain, England and Belgium. In Brussels, he creates a gym he runs for seven years. Aged 35, he did develop a beautiful room in Paris. Compromise in 1870 - 1871, at the time of the "common", he was interned, released a few months later, he assures the direction of a smaller gym, until 1879, two years before dying at age 69.
Outside of a few installments, there is unfortunately little of the method Triat and its major projects. The working group sessions or in
iduel he organized included some exercises in hands free, with bar-bells six kg dumbbells, racing, jumps, but also for more advanced students of weightlifting movements, such as torn, developed , supported and threw in one or both hands.

Around 1880, the first associations are born in Germany in Hamburg, Cologne, Leipzig, Frankfurt, Duisburg, Munich. Ttrois movements are performed:
- A run of stone;
- Raise a pig in resistance;
- A focused very heavily.
In Russia, St. Petersburg, Dr. Krajewski finds himself on the Benefits of the rising weight and created in 1885, the "circle of friends weightlifting.
In the late nineteenth century, the first global ranking of the strongest men is established. For the Athens Olympics in 1896, weightlifting program is among the sports optional, but the Baron Pierre de Coubertin who deserves the credit for the renovation of "games" after 1503 years of interruption, seems to ignore inclusion of the sport to the Olympic program. No French weightlifter, any more than Germans, not participating in these competitions. Two movements are then enrolled in the program: the clean and jerk to both arms and the clean and jerk an arm, respectively won with 111.5 kilograms and 71 kilograms. Regarded as the strongman of the royal family, Prince George of Greece considers these events ...
Weightlifting is included for the first time in the Olympic program in 1920, although first gold medal was already awarded in 1896 and 1904 in category "heavy". The first women's World Championships were held in 1987. The women lifters made their entry into the Olympic movement in 2000.
The International Weightlifting Federation (IWF) was founded in 1905 and currently has 167 member countries. The French federation of weightlifting, bodybuilding and bodybuildingIt was created in 1914 as the Federation of French weights and originated the Weightlifting Club of France, founded in 1896.
Key Dates1914 Creation of the French Federation of Weights and Dumbbells by Jules Rosset.
1920 Creation of an International Federation by the same Jules Rosset.
1925 Formalization of weightlifting final at the Olympics with 3 movements in both arms.
- Developed - Torn Shoulder-cast with 5 categories of body weight of the pen (60 kg) Heavyweight (+ 82.5 kilograms).
1952 Creation of 2 categories of additional body weight, or 7 categories: cock (56 kg) Heavyweight (+90 kg).
1968 Creation of 2 additional categories to 9 categories: Fly (52 kg) Heavyweight (110 kilograms).
1968 Creation of awarding a medal and total movements.
Removing the 1972 Olympic Development.
1976 Creation of a tenth category, the 100 kg category Naming by numbers (before: fly, cock feather, light, medium, medium heavy, heavy, light, heavy, medium, heavy, super heavy).
1980 Formalization of an international listing table (table IWF), to compare all categories.
1984 Formalization of women's weightlifting with nine categories (44-48-52-56-60-67,5-75-82,5 - 82.5).
1987 First hhampionnat World fééminin (first Miami USA).
1992 Changed all categories of body weight which becomes: 54-59-64-70-76-83-91-99-108 - 108 for men; 46-50-54-59-64-70-76 -83 to 83 for women
1997 Introduction to Women's Olympic program
1998 Change categories of body weight with 8 categories for men: 56-62-69-77-85-94-105 - 105 for men. 7 categories for women who become: 48-53-58-63-69-75 - 75.

Weightlifting combines strength, flexibility and speed.
Competitions are organized by categories of weight lifters. It runs 2 successive movements: the snatch and the clean and jerk. He is entitled to 3 trials for each movement. The total score of 2 movements determines the ranking.
Until 1928, the competition included only raise an arm. Today, it includes in the order two levers: the snatch and the clean and jerk. The various categories indicate body weight.
- By 1972, lifting weights just by taking hands.
- Since 1972, weightlifting competition: bring a barbell at arm's length
At one time: the snatchThe bar is placed horizontally in front of the legs of the athlete. It must grab the hands pronated and pull of a single movement of the tray until the end of arms stretched above his head. The motion carried, either by bending or splitting the legs. The bar is along the body of an uninterrupted movement, and no other party that their feet touch the plate. The weight lifted should be kept motionless, arms and legs outstretched, feet aligned to signal to place the bar on the shelf. The turning of the wrists should be done only when the bar exceeded the top of the athlete. The athlete stands up as soon as possible, placing the feet at right angles to the trunk and the barbell. The signal must be given once the athlete is still all parts of his body.
Two-step : The clean and jerk (first at the shoulder, then over the head with his arms outstretched).First part, the shoulder bar is placed horizontally in front of the legs of the athlete. It must grab the hands pronated and pull a single movement of the plate to the shoulders. This movement occurs, either by bending or splitting the legs. During this continuous movement, it is possible that the bar slides along the thighs, but it does not touch the chest before the final position when it rests on the clavicles or on the chest above the nipples or the arms folded completely. The athlete stands up whenever he can by placing the feet aligned and perpendicular to the trunk and the barbell.
Second part, the Jerk: The athlete bends the legs and simultaneously performs a push with the legs and arms to bring the dumbbell to the end of the arm stretched vertically above the head. The weight lifted should be motionless, arms outstretched legs and feet aligned, until the referees signal to place the dumbbell on the shelf. The signal from the referees must be given once the athlete is still all parts of his body.
The "Total Olympic" consists of the addition of the two best performances in these two exercises are the only recognized competition. FacilitiesThe movements are performed on a square wooden 4 meters wide. Any movement in which an athlete sets foot outside the plate will be declared invalid.
Equipment Equipment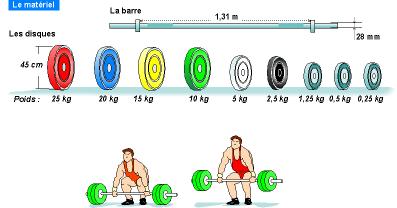
The bars must have the following dimensions:
1. distance between disks: 1.31 m minimum;
2. wide collar on the inside collar of the sleeve includes: at least 20 mm, 40 mm maximum;
3. total length without sleeves: 2.20 m maximum;
4. bar diameter: 28 mm;
5. diameter of the sleeve least 50 mm, maximum 55 mm;
6. diameter of the largest disk: 45 cm;
7. weight of the heavier disc: 25 kg;
8. weight bar and collars: 25 kg;
9.The discs should have a diameter of 45 cm and be colored red (25 kg), blue (20 kg), yellow (15 kg). They must be of smaller diameter for the 10 kg, 5 kg, 2.5 kg, and 1.250 kilograms and record discs (1 kg, 0.5 kg and 0.25 kg);
10.tous disks must have a clear indication of their weight;
11.The disk must be placed on the bar in descending order, the largest inside, arranged so that the referee can read the numbers on each disc. They must be kept in position by a neck.
In order to record smaller disks can be added to the bar to give a total weight of at least 1 / 2 kg more than the current world record.

When a competitor wears a belt, the width thereof shall not exceed 12 inches. Ban on wearing a belt under the shirt or dress.
BandagesBands or rubber materials or rubber materials are prohibited.
Wristbands
It is possible for athletes to wear gauze bandages or medical crepe. Bandages leather can be worn.
Kneeling
Gauze bandages or medical crepe can be worn. Alternatively, an elastic brace may be worn. Wearing both simultaneously is prohibited.
Body
The bandages around the body are prohibited. Sticking plasters applied locally to injured muscles must be performed by Dr. official IWF service.
Hands
The plasters on his fingers or hands inside are forbidden. If there are injuries to the inside of the hands, plasters can be applied both inside and on the back of the hand by Dr. official IWF service.
Inches
Bandages gauze or crepe with a length of 30 cm maximum can be worn, but their width can not exceed the length of the thumb.
The main rules CategoriesThe categories are based on the weight.
The weight classes have undergone changes since 1920. Since January 1998, there are eight categories for competitors older men and seven women. All competitions under the rules of the IWF should follow this order of weight without rearranging the order of events.
Men Women
1. 56 kg 48 kg
2. 62 kg 53 kg
3. 69 kg 58 kg
4. 77 kg 63 kg
5. 85 kg 69 kg
6. 94 kg 75 kg
7. 105 kg Over 75 kg
8. Over 105 kg
ProgramThe IWF acknowledges the following movements, which must be made in this order, without an interval between movements in all competitions under the rules of the IWF:
- Ripped from the arms;
- Shoulder and threw two arms.
The IWF also recognizes world records the same movements and totals for seniors and juniors.
The snatch two armsFeatures
The bar is placed horizontally in front of the legs of the athlete, grasp and pull a single shot at the end of the earth outstretched arms vertically above the head, either by "splitting" or bending on legs.
The bar will move from one continuous movement along the body with any party other than the feet can not touch the ground during the execution of movement.
The weight lifted must be maintained in the final motionless position, arms and legs outstretched, feet on the same line until the referee's signal to rest the bar on the shelf.
The turning of the wrists should take place only when the bar exceeded the top of the head of the performer.
The athlete "slot" or "bending" can perform recovery at its convenience by having his feet on the same line, parallel to the plane of his body and the bar.
The signal the referee will be given once the athlete is completely immobile.
Incorrect Movements:
- Draw suspended.
- Time off during the ascent of the bar.
- Extension of illegal arms.
- Extension arm incomplete.
- Termination in "developed".
- Flexion and extension of the arm during the recovery.
- Contact ashore knee, buttocks or any body part other than feet.
- Release of the plateau during the execution of movement, ie touching the surface off the board with any body part.
- Drop the bar before the referee's signal to the rest bar.
- Do not have feet on the same line parallel to the stem and bar.

1. Stage 1: supported
The bar is placed horizontally in front of the athlete's legs, grasping hands in pronation and get one time to land on the shoulders or bending the legs, or splitting.
The bar should not touch the chest before the final position, then it will rest on the collarbone or chest or arms bent at the bottom.
Bring your feet on the same line, legs outstretched, before execution of the runner. The athlete can make this change to her liking.
2. 2nd time: cast
Flex the legs and relax and the arm to bring the bar at the end of arms stretched vertically.
Bring your feet on the same line, arms and legs outstretched, and wait for the referee's signal to rest the bar on the shelf.
The signal the referee will be given once the athlete is completely immobile and has his feet on the same line, parallel to the plane of his body and the bar.
3. Important Note
After the clean and laid before the athlete can secure the position of the bar.
This should not be confusing. It can be in any case to grant a second time to the athlete, but to authorize:
- Either to withdraw his thumbs or décrocheter he used this system;
- Or, if the bar is set too high and the embarrassment in his breathing or cause pain, to descend to land on his shoulders;
- Either to change the spacing of his hands.
4. Incorrect Movements:
Backed
- Any unfinished attempt in which the bar is reached knee height.
- Draw suspended.
- Backed by two or more movements.
- Contact ashore knee, buttocks or some parts of the body other than feet.
- Fully supported in which the bar would come into contact with part of the trunk before the definitive position on the shoulders.
- Shoulder flexion, elbow or contact senior arms on knees or thighs.
- Release of the plateau during the execution of movement, ie touching the surface off the board with any body part.
Thrown
- Any apparent effort to cast is not complete.
- Extension of illegal arms.
- Downtime for extending the arms.
- Flexion and extension of the arm during the recovery.
- Release of the plateau during the execution of movement, ie touching the surface off the board with any body part.
- The bar rested on the shelf before the referee's signal.
- Drop the bar before the referee's signal to the rest bar.
- Do not have feet on the same line, parallel to the stem and bar.
General Regulations for all movementsIt will be awarded a total of two minutes to athletes, since the call of their names until their trials. After a minute, it will signal to warn.
If at the end of two minutes the athlete has not yet raised the bar of the plateau to its test, this test will be invalidated.
If an athlete did two tests one after the other, we had three minutes for the next test and we will signal to the second minute.
If after three minutes, the athlete has not raised the bar of the shelf to his essay, this movement will be invalidated.
The time limit for a fourth test out of competition will be three minutes. It will signal to the second minute.

It is a sport that is parallel rather focus on pure strength and not on the survey techniques as in weightlifting.
There are 3 disciplines in which athletes compete:
- The bench press or bench press.
- The squat: the athlete raises the bar and lay behind his neck.
- The dead lift or lifted off the ground.
Copyright Sportquick/Promedi

 |
Championne olympique des -87 kg en 2021. Championne du monde des -76 kg en 2018 et des -87 kg en 2019 (2eme en 2022). Championne d'Asie des -75 kg en 2015 et des -97 kg en 2019 et 2020. ... |






(11).jpg)







